Forex Trading: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners

Forex Trading: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
Introduction to Forex Trading
Forex trading, or foreign exchange trading, is the act of buying and selling currencies to profit from fluctuations in their exchange rates. It operates in the largest and most liquid financial market globally, with massive daily trading volumes. This guide provides beginners with a clear, concise understanding of forex trading, covering essential concepts, strategies, and tips to start effectively and responsibly.
Understanding the Forex Market
The forex market is a decentralized global marketplace where currencies are traded. Unlike stock markets, it operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, due to overlapping time zones across major financial centers like London, New York, Tokyo, and Sydney. Participants include banks, institutions, and individual traders, all aiming to capitalize on currency price movements.
Key Concepts in Forex Trading
To navigate forex trading, beginners must grasp fundamental terms:
- Currency Pairs: Currencies are traded in pairs, such as EUR/USD (Euro vs. US Dollar). The first currency is the base, and the second is the quote currency. The price indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency.
- Pip: A pip (percentage in point) is the smallest price movement in a currency pair, usually the fourth decimal place (e.g., a change from 1.1050 to 1.1051 is one pip).
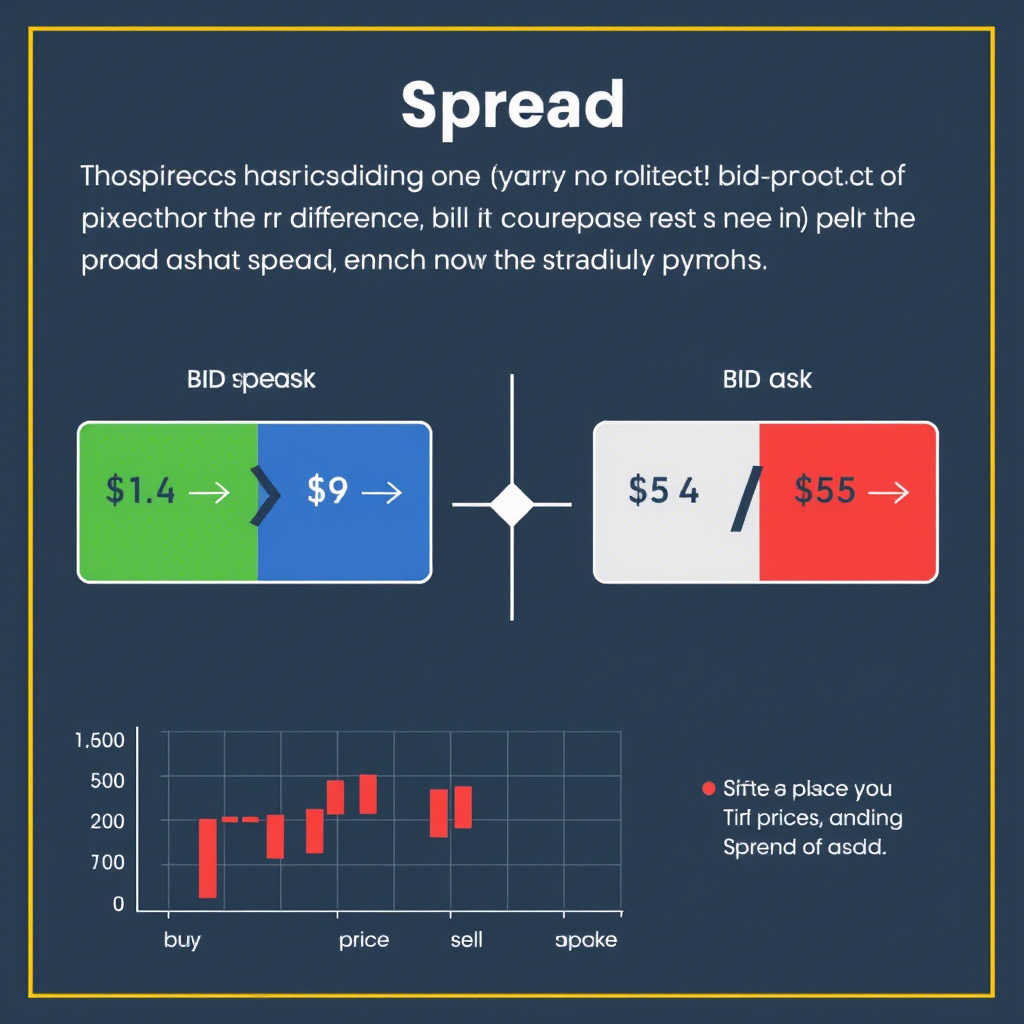
- Spread: The difference between the bid (sell) price and ask (buy) price. This is the broker’s commission for facilitating trades.
- Leverage: Leverage allows traders to control larger positions with less capital. For example, 100:1 leverage means $1,000 controls a $100,000 position. While it boosts potential profits, it also magnifies losses.
- Margin: The amount of money required to open a leveraged position, acting as a deposit.
- Lot Size: Forex is traded in lots. A standard lot is 100,000 units of the base currency, while a mini lot is 10,000 units.
How Forex Trading Works
Forex trading involves predicting whether a currency pair’s value will rise or fall. Here’s a step-by-step process for beginners:
- Select a Broker: Choose a regulated broker with a reliable platform, low spreads, and good customer support.
- Open an Account: Start with a demo account to practice without financial risk or a live account for real trading.
- Analyze the Market: Use two primary methods:
- Technical Analysis: Study historical price charts using tools like moving averages, Relative Strength Index (RSI), or candlestick patterns to predict future movements.
- Fundamental Analysis: Monitor economic indicators (e.g., interest rates, GDP, employment data) and geopolitical events that influence currency values.
- Place Trades: Decide to buy (go long) if you expect the base currency to strengthen or sell (go short) if you predict it will weaken.
- Monitor and Close Trades: Use stop-loss orders to limit losses and take-profit orders to secure gains.
Strategies for Beginners
- Trend Following: Identify and trade in the direction of the market trend using tools like moving averages.
- Range Trading: Trade within a defined price range, buying at support levels and selling at resistance levels.
- Breakout Trading: Enter trades when the price breaks through key support or resistance levels, signaling a potential trend.
- Scalping: Make quick, small trades to capture minor price movements, requiring intense focus and fast execution.
Risk Management
Forex trading carries significant risks due to market volatility and leverage. Key risk management practices include:
- Position Sizing: Risk only 1-2% of your account balance per trade to avoid large losses.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Set automatic exit points to limit losses if the market moves against you.
- Avoid Overleveraging: Use leverage cautiously to prevent wiping out your account.
- Emotional Discipline: Stick to your trading plan and avoid impulsive decisions driven by fear or greed.
Tips for Success
- Practice with a Demo Account: Gain experience without risking real money.
- Develop a Trading Plan: Outline your goals, risk tolerance, and strategy to maintain consistency.
- Stay Informed: Follow economic news and global events that impact currency markets.
- Keep a Trading Journal: Record your trades to analyze successes and mistakes.
- Be Patient: Forex trading requires time to master; avoid chasing quick profits.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
- Overtrading: Trading too frequently or with large positions can lead to losses.
- Ignoring Risk Management: Failing to set stop-losses or risking too much capital is a recipe for disaster.
- Emotional Trading: Letting emotions like greed or fear dictate decisions often results in poor outcomes.
- Lack of Education: Trading without understanding the market increases the likelihood of failure.
Getting Started
- Educate Yourself: Study forex basics through books, online courses, or tutorials.
- Choose a Platform: Popular platforms like MetaTrader 4 or 5 offer user-friendly interfaces and robust tools.
- Start Small: Begin with a small account and low-risk trades to build confidence.
- Stay Disciplined: Follow your strategy and avoid deviating based on short-term market noise.
Conclusion
Forex trading offers exciting opportunities but demands knowledge, discipline, and patience. Beginners should focus on education, practice, and risk management to build a strong foundation. By starting small, using demo accounts, and adhering to a well-thought-out plan, you can navigate the complexities of the forex market and work toward consistent profitability. Always approach trading with caution, as the high potential for rewards comes with equally high risks.